Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Mihova D. AMKL M7. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiam7.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL, M7)
- Up to 10% of AML in children, 5% or less of adult AML (Orphanet (May 2004): Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia [Accessed 6 April 2018])
- See also Myeloid leukemia associated with Down syndrome
- Associated with marrow fibrosis due to megakaryoblast secretion of fibrogenic cytokines, which makes marrow aspiration difficult
- In adults, median age 57 years, 59% have prior hematologic disorder or myelodysplastic syndrome (Blood 2006;107:880)
- 19% had prior chemotherapy, classify now as AML-MRC (myelodysplasia related changes) or t-AML
- Survival: poor, median overall survival is 6 months
- Peripheral blood: often contains micromegakaryocytes and atypical platelets
- Down Syndrome (DS): 150x increased risk of AML compared to non-Down children age 0 - 4 years; 70% are AML M7 compared to 3 - 6% in non-Down children
- DS children ages 0 - 3 years: ALL vs AML risk is 1:1.2 compared to 4:1 for non-DS children
Clinical features
- Thrombocytopenia, may have thrombocytosis, dysplastic features in neutrophils, erythroids, megakaryocytes and platelets
- Infrequent hepatosplenomegaly
- Associated with germ cell tumors in young boys
Diagnosis
- WHO 2008: 20%+ blasts
- 50%+ blasts of megakaryocytic lineage are present in bone marrow
- Must exclude AML-MRC (myelodysplasia related changes), AML with t(1;22)(p13;q13); inv(3)(q21;q26.2); t(3;3)(q21;q26.2) and Down syndrome related
- Megakaryocytic lineage is based on CD41+, CD61+ or positive platelet peroxidase reaction on EM
Case reports
- 17 month old girl with bi-allelic deletions within 13q14 and transient trisomy 21 with absence of GATA1 (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2011;57:516)
- Young boy with coexisting mediastinal germ cell tumor (Clin Transl Oncol 2007;9:329)
- 25 year old man with findings on FNA and CSF (Cytojournal 2011;8:17)
- 25 year old man with i(12p) related disease after primary mediastinal germ cell tumor (J Korean Med Sci 2011;26:1099)
- 58 year old woman with coexisting myeloid sarcoma of femur (Srp Arh Celok Lek 2011;139:805)
- Diagnosis 15 years after kidney transplantation (Ann Hematol 2011;90:843)
- "Cannibalistic" phagocytosis in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AML M7) with t(10;17)(p15;q22) (Leuk Lymphoma 2010;51:1944)
- Coexistence of meningeal infiltration and multiple lymphadenopathy as the initial presentation of de novo adult acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (Leuk Res 2011;35:e50)
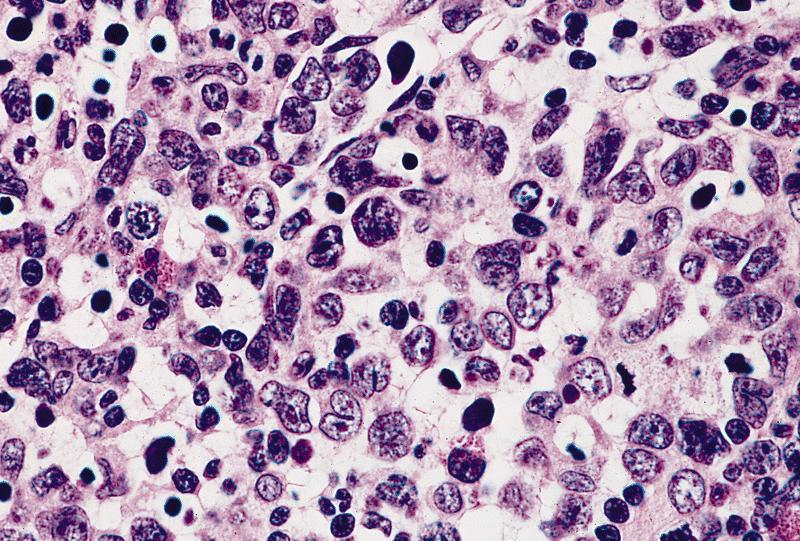
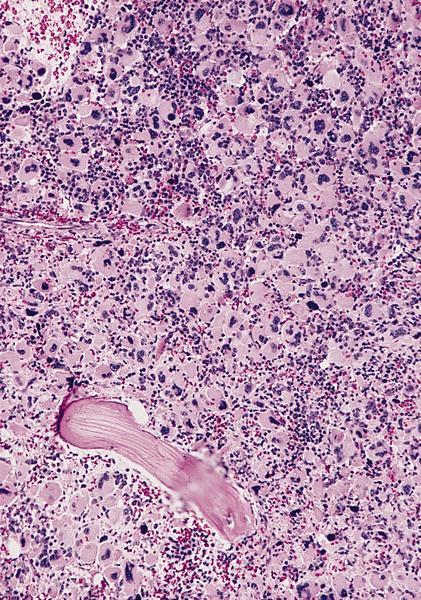
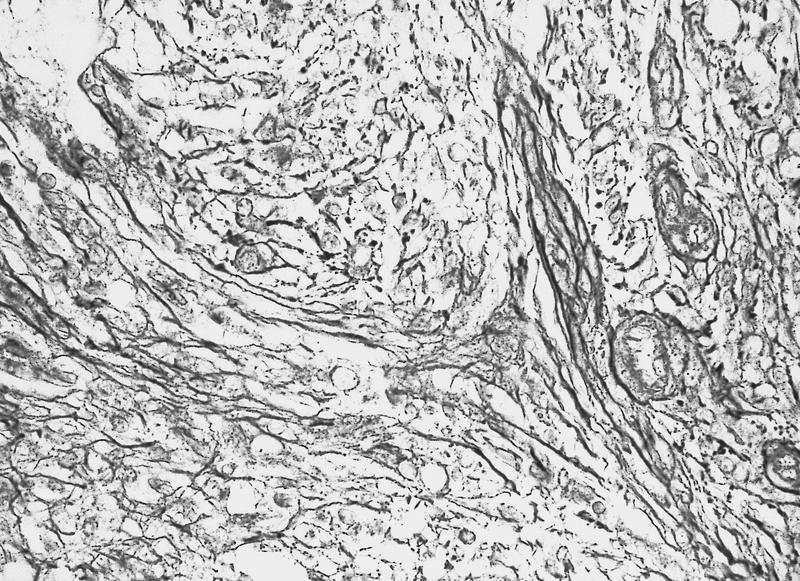
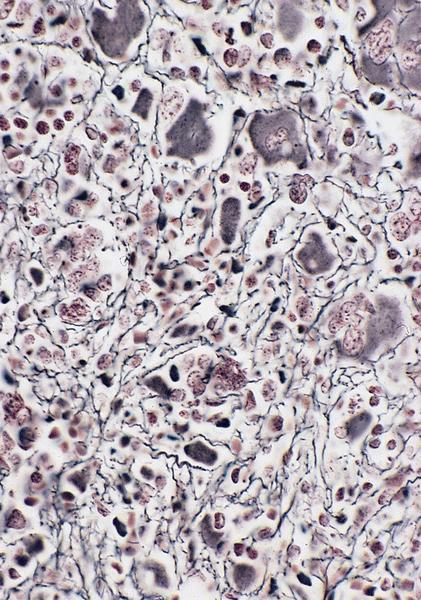
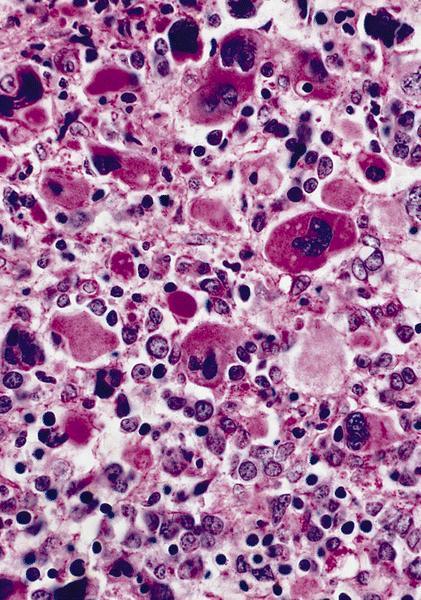
Microscopic (histologic) description
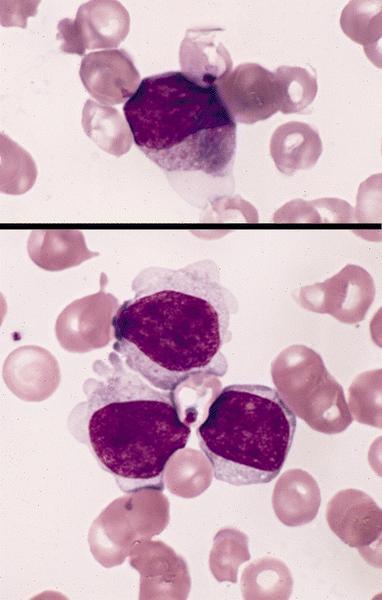
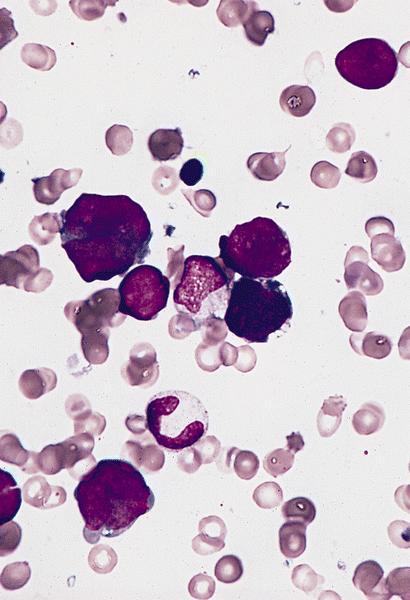
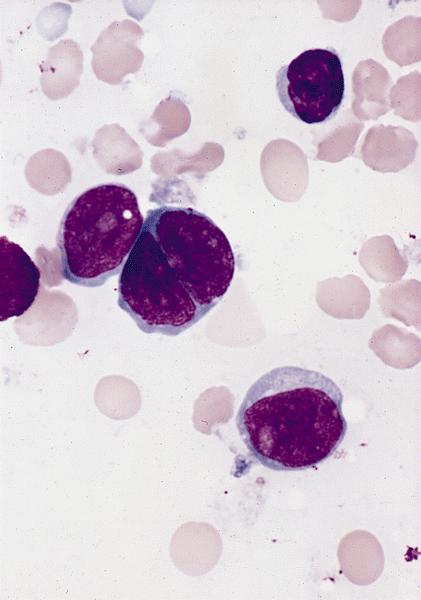
- Megakaryoblasts (often better morphology on biopsy than smear) are medium / large cells with blue vacuolated, agranular, eosinophilic cytoplasm containing fine granules, cytoplasmic projections (blebs and pseudopods) resembling platelets, irregular cytoplasmic borders and cytoplasmic zoning; may occur in clusters
- Nuclei are round or slightly indented with finely reticular, dense chromatin and 1 - 3 nucleoli
- Myelofibrosis or increased marrow reticulin is common; may also have small lymphoid-like blasts
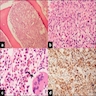
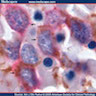
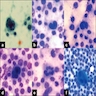
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
- CD41 and CD61 (megakaryocyte specific), CD42b (Mod Pathol 2005;18:603), CD34, CD36, factor VIII and von Willebrand factor
- Variable CD13, CD33, CD71, alpha naphthyl acetate esterase, PAS and HLA-DR
- Rarely positive for alpha-1-antitrypsin, alpha-1-antichymotrypsin or lysozyme (Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:883)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Megakaryoblasts have demarcation membranes and “bulls-eye” alpha granules with peroxidase activity in nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum, but not in granules and Golgi complex